本网讯 近日,我校先进土木工程材料科研团队张高展副教授联合青岛理工大学侯东帅教授和武汉理工大学丁庆军教授等在《Cement and Concrete Composites》(中科院1区,影响因子7.586)上发表题为“Unraveling the microstructural properties of cement-slag composite pastes incorporated with smart polymer-based corrosion inhibitors: From experiment to molecular dynamics”的研究论文(https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2021.104298,《Cement and Concrete Composites》简称CCC,与《Cement & Concrete Research》并列为建筑材料领域两大顶级期刊)。
文章从实验和分子动力学模拟两个角度阐明了侵蚀性离子传输抑制剂调控海洋侵蚀环境下硅酸盐水泥-矿渣复合浆体微结构的形成机理,为海工混凝土的防腐耐蚀设计提供了一定的理论依据。侵蚀性离子传输抑制剂能够显著提升胶凝浆体中小孔数量,有效改善胶凝浆体孔结构,尤其在海水侵蚀环境下,侵蚀性离子传输抑制剂的掺加对提升胶凝浆体的抗海水侵蚀能力有重要意义。
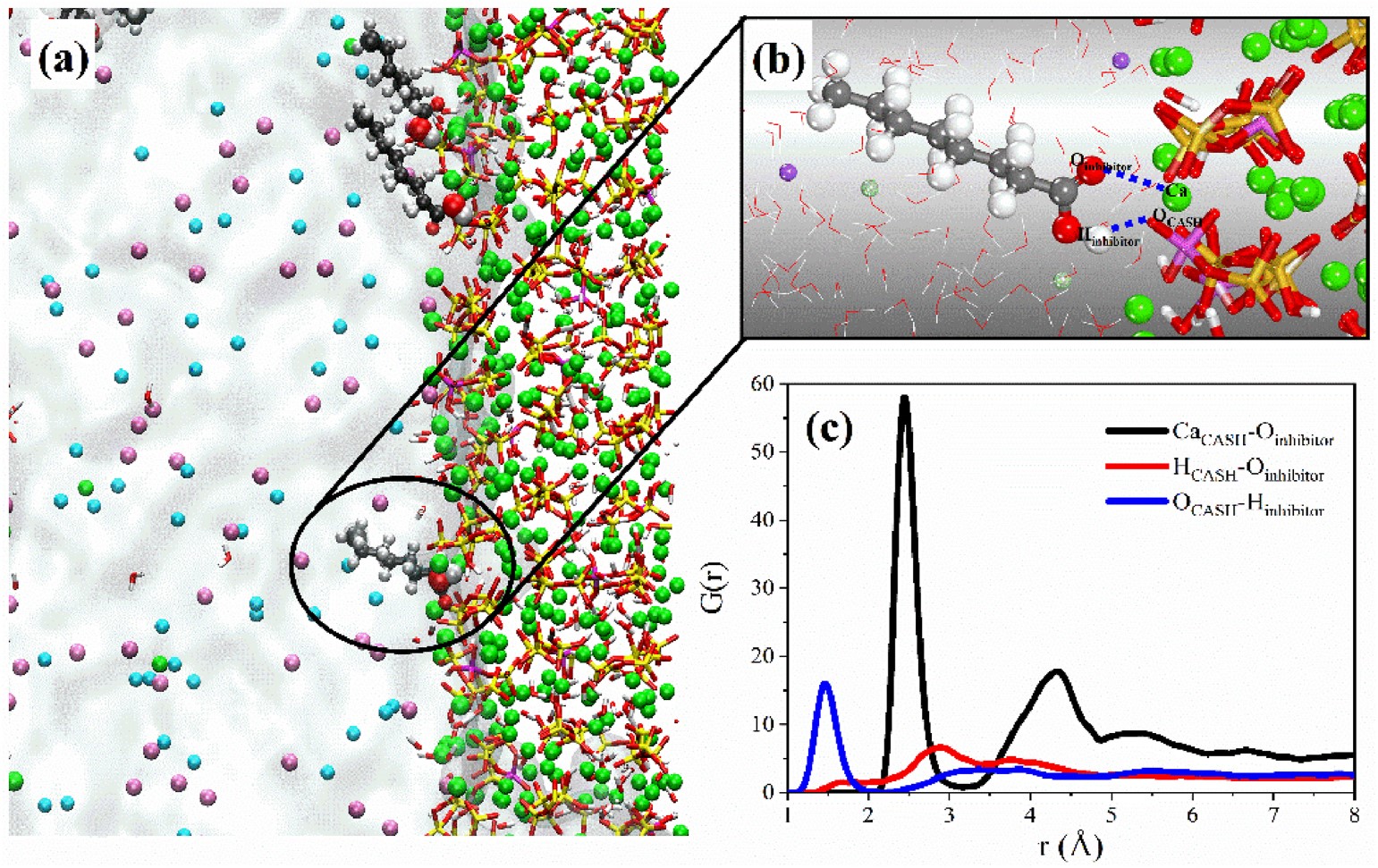
Fig. 1 Schematics of (a) the corrosion inhibitor molecules adsorbed on the CASH surface and (b) the bonding relationship between the corrosion inhibitor molecule and the CASH surface, (c) radial distribution functions of Ca CASH -O inhibitor , H CASH -O inhibitor , and O CASH -H inhibitor pairs.
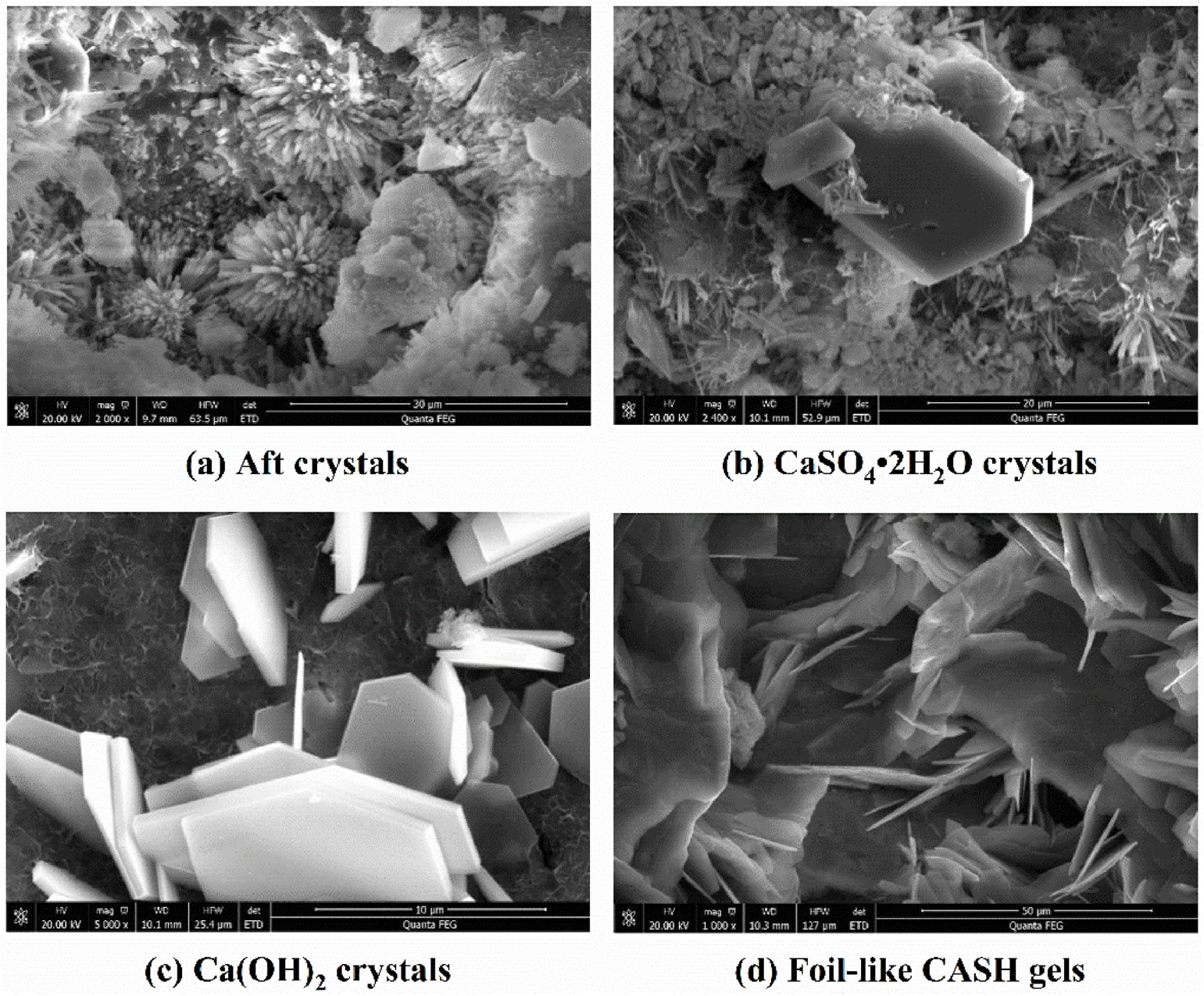

Fig. 2 SEM spectra of the hydration products in the cement-slag composite pastes.
该论文由我校与青岛理工大学、武汉理工大学联合完成,安徽建筑大学为第一署名单位,该成果得到了国家自然科学基金面上项目(51878003)的资助,是学校先进建筑材料科研平台建设和科学研究取得的重要成果。



